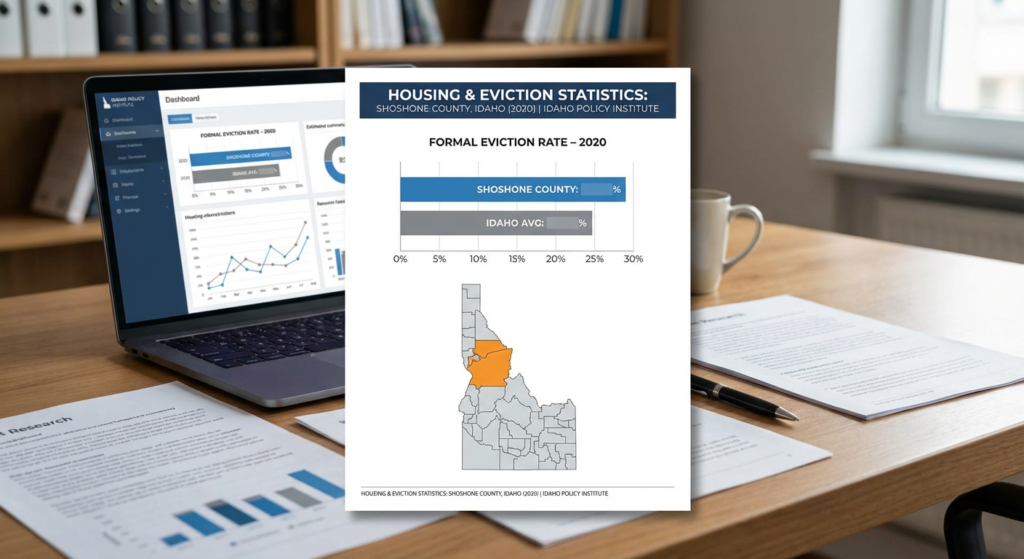
Introduction to Shoshone County eviction trends
Overview of Idaho Policy Institute data
This report captures significant shifts in eviction rates during 2020. It highlights how national events impacted local communities, bringing underlying issues to light.
Notably, IPI’s data includes metrics on formal eviction filings and outcomes. This provides stakeholders interested in understanding tenant rights and landlord responsibilities with an informed picture.
The research also examines demographic variables influencing these rates. By identifying vulnerable populations, policymakers can better address the root causes of housing instability in Shoshone County.
Such insights are vital for crafting effective solutions to reduce future evictions and foster community well-being throughout Idaho.
Key statistics from 2020
Data from the Idaho Policy Institute revealed that over 200 eviction cases were filed in the county during this period. A substantial portion of these cases stemmed from non-payment of rent, highlighting financial instability among many residents.
Interestingly, female-led households accounted for nearly 60% of all evictions. This statistic underscores vulnerabilities within specific demographics during challenging times.
Moreover, a notable increase in filings occurred between March and December 2020. These months coincided with heightened COVID-19 restrictions, which exacerbated existing housing challenges for many families across Shoshone County.
Comparison with previous years
In contrast, the years leading up to 2019 had relatively stable eviction rates—the steady decline during that period provided hope for many residents struggling with housing insecurity.
However, the spike in 2020 highlights vulnerabilities within the community. Economic pressures from job losses and rising living costs have taken their toll on households across demographics.
The difference between these periods reveals much about changing circumstances in Shoshone County. Such insights can help stakeholders understand ongoing needs and craft effective responses moving forward.
Demographic breakdown of evictions
Additionally, low-income households are disproportionately represented among those facing formal eviction processes. This group often struggles with unexpected expenses and job instability, making it challenging to keep up with rent payments.
Racial and ethnic minorities also experience significant disparities in eviction rates. Systemic issues contribute to these inequalities, highlighting the need for targeted interventions.
The age distribution shows a notable concentration of evicted individuals aged 25-34. Many of these young adults are navigating an unstable job market while trying to establish their independence.
Recognizing these demographics helps stakeholders tailor resources and policies to effectively address the needs of those affected by housing instability in Shoshone County.
Factors contributing to eviction rates
Housing affordability is another pressing issue. With rising rent prices, many families find it difficult to keep up with payments. This creates a cycle of late fees and potential legal action.
Additionally, lack of access to supportive resources can exacerbate situations. Many affected individuals may not know where to seek help or what options are available.
The local rental market also influences these trends. A shortage of affordable housing units limits choices for those at risk of eviction, leading them toward more precarious living situations.
Understanding these contributing factors is essential for addressing the high eviction rate reported by the Idaho Policy Institute in 2020.
Policy implications
With a noticeable rise in formal evictions, policymakers should consider implementing preventive measures. Strategies like rental assistance programs or mediation services could help tenants and landlords find common ground before disputes escalate.
Moreover, tenant rights awareness campaigns can empower residents facing potential eviction. By providing resources and education, communities may reduce the stigma surrounding financial hardship.
Collaboration with non-profit organizations is essential for developing sustainable solutions. Engaging local stakeholders will foster a unified approach toward tackling the root causes of evictions in Shoshone County.
Continuous assessment of housing policies based on data-driven insights will ensure that efforts align with community needs and changing economic landscapes. Such proactive steps are crucial for fostering long-term housing security in the region.
Community impact
Schools also feel the ripple effects. Children experiencing displacement may struggle academically due to stress and uncertainty at home. This can lead to lower graduation rates, perpetuating a cycle of poverty.
Economic implications are significant as well. Landlords may experience fluctuating rental income, while neighborhoods can become less stable due to higher tenant turnover.
Community cohesion suffers when long-term residents have to relocate frequently or are forced out entirely. Local businesses might experience reduced patronage from displaced individuals who can no longer afford to live nearby.
Rising formal eviction rates reshape the very fabric of life in Shoshone County, affecting everyone involved—residents, service providers, and local economies alike.
Recommendations for stakeholders
Implementing educational programs is essential. These initiatives should focus on tenant rights and financial literacy to empower residents facing housing instability.
Encouraging proactive communication with landlords can reduce misunderstandings. Regular forums or workshops facilitate dialogue that leads to mutually beneficial outcomes.
Funding for emergency rental assistance should be increased. This would help families avoid eviction during times of crisis, ensuring they have a safety net when they need it most.
Tracking and analyzing eviction data more thoroughly will provide insights into patterns and emerging issues. Stakeholders can use this information to tailor interventions that directly address the specific needs within the community.
Conclusion
Understanding these statistics can help communities and policymakers address the pressing issues surrounding evictions. As we reflect on the demographic breakdown and contributing factors, it becomes clear that targeted interventions are essential.
Community stakeholders must come together to develop strategies that not only mitigate eviction rates but also support families facing housing insecurity. With careful planning and collaboration, there is an opportunity for positive change that benefits everyone involved.
Given the Shoshone County formal eviction rate in 2020, the Idaho Policy Institute’s findings will be crucial as we move forward toward a more stable future for all Shoshone County residents.